half life formula pharmacology
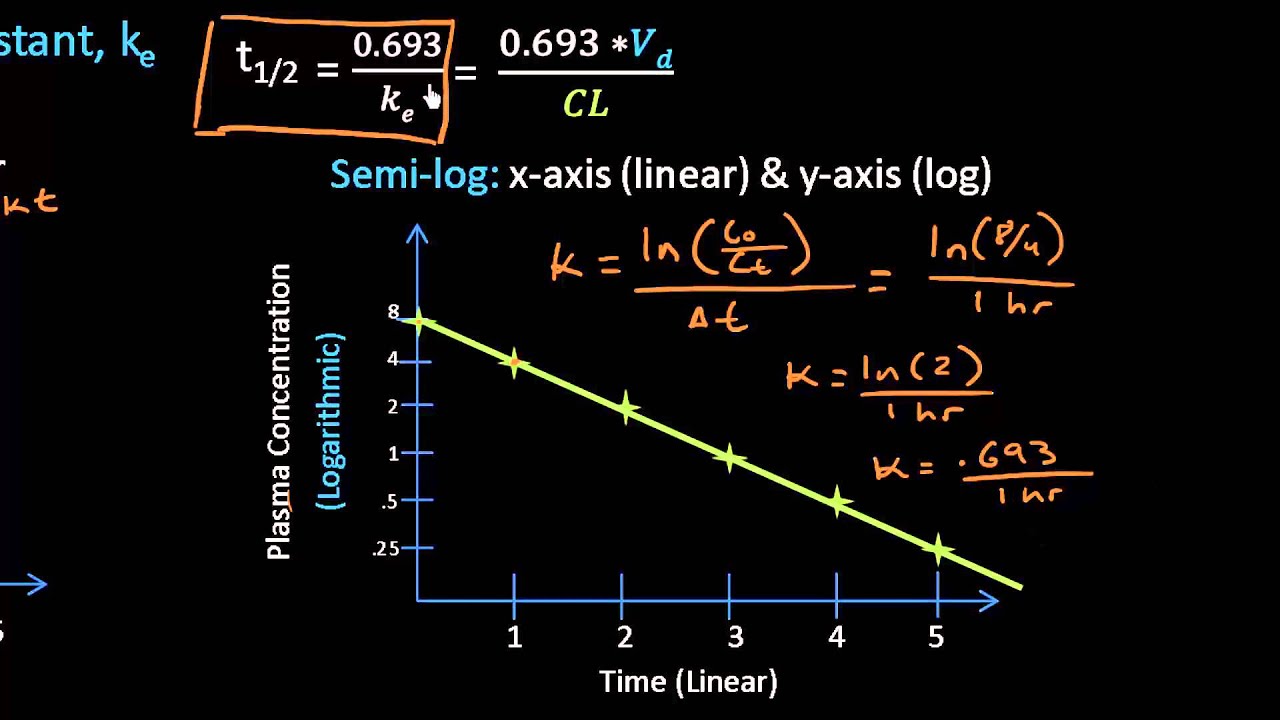
λ is the slope of the. T120693Volume of DistributionClearance As demonstrated by the formula a drugs half-life is directly dependent on its volume of.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
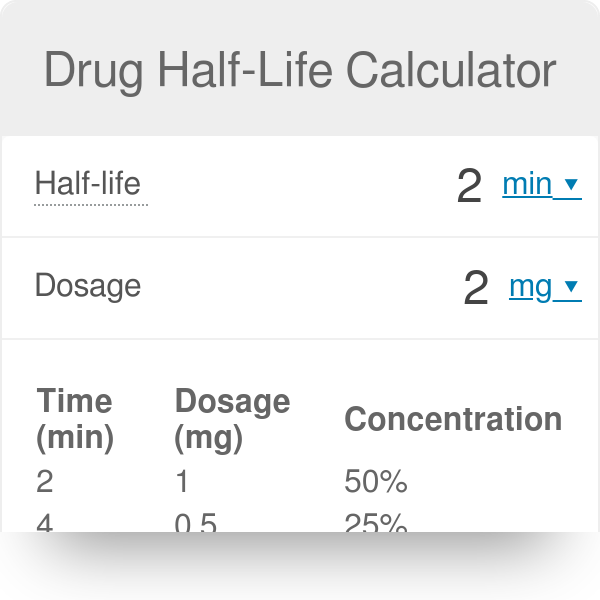
. Describe formulas conversions and other math calculations in pharmacology Provide a description of half-life in pharmacology Define the margin of safety in pharmacology. Half-life t 12 is the time required to change the amount of drug in the body by one-half during elimination or during a constant infusion. An exponential decay can be described by any of the following four equivalent formulas.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. Half-life t 12 1. Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half.
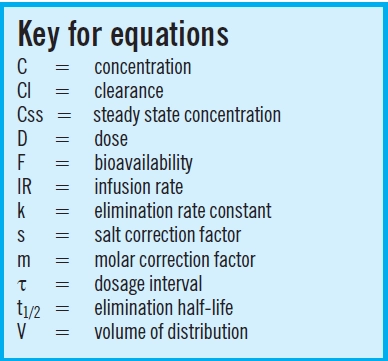
Pharmacology math tutorial for quick exam review. Half-life t Vd CL k kee 12 0693 2 0693 ln. N0 is the initial quantity of the substance that will decay this quantity may be measured in grams moles number of atoms etc Nt is the quantity that still remains and has not yet decayed after a time t.
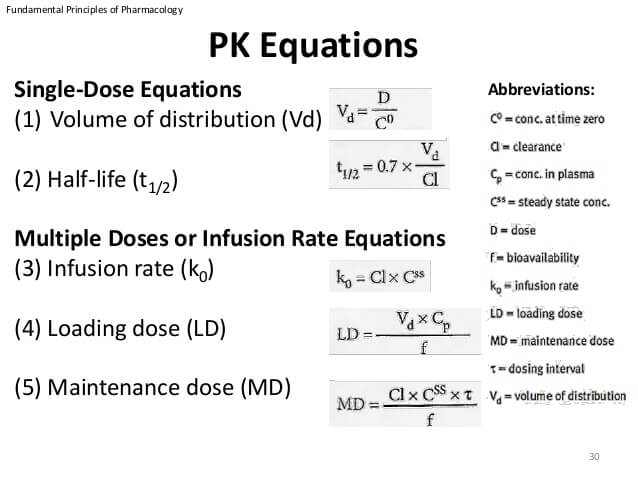
Heres the formula for half-life. Ian Lord Show bio. Half-life is determined by clearance CL and volume of distribution V D and the relationship is described by the following equation.
The half-life can be computed simply by dividing the slope of the curve into 0301 the difference between the logarithm of a number C and the logarithm of number half as large C2. T 1 2 ln 2 V D C L displaystyle t_frac 12frac. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are.
Science Courses Introduction to Pharmacology Course Formulas Calculations for Pharmacology Chapter Half-Life in Pharmacology Instructor. For more tutorials see our pharm playlist at. By definition t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall by one half.
This rate is constant in first-order kinetics and is independent of drug concentration in the body. From this equation we see that the key determinants of half-life are the Volume of Distribution and the Clearance which we now can calculate if we have the. In the simplest caseand the most useful in.
T 12 069 x VdCL. Fractional rate of drug removal from the body. Intravenous bolus Initial concentration C D 0 Vd Plasma concentration single dose CCe kte 0 ae Plasma concentration multiple dose C Ce e.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol. Elimination rate constant λ. For drugs with first order kinetics this is a constant.

Drug Half Life Explained Calculator Variables Examples
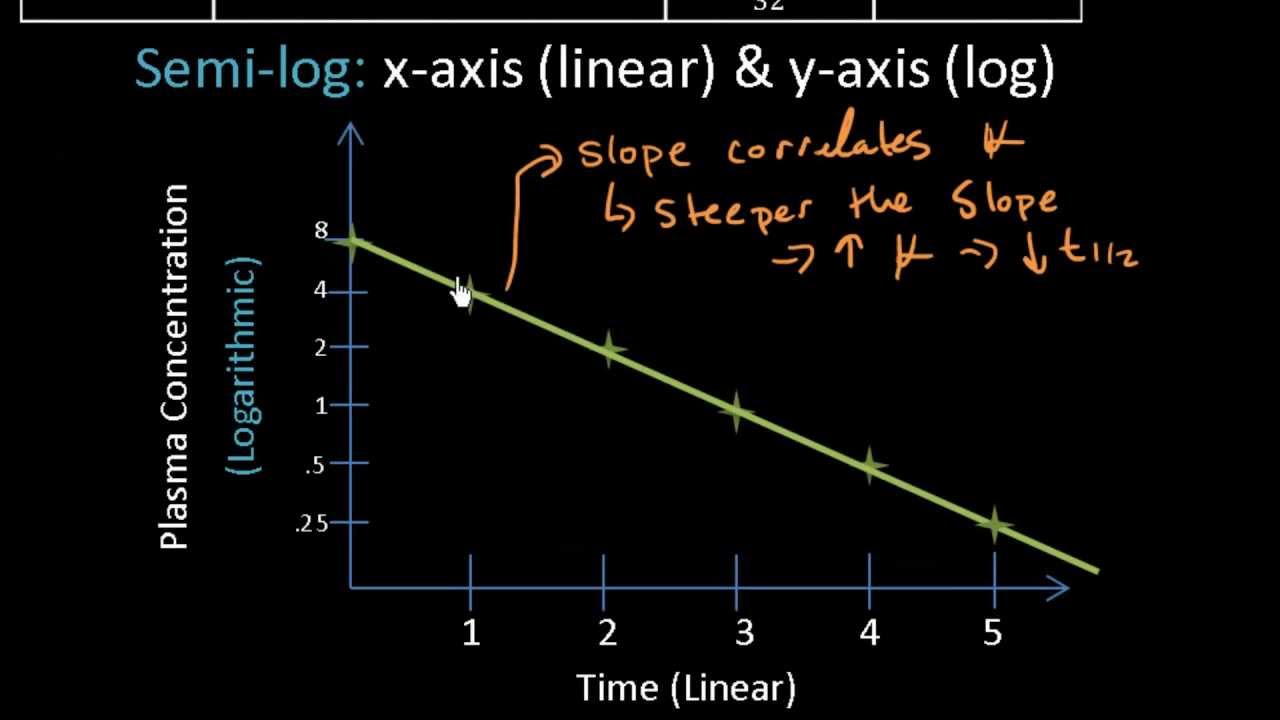
Drug Half Life An Overview Pharm Lect 10 Youtube
Back To Basics Pharmacokinetics The Pharmaceutical Journal

Elimination Half Life An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Half Life Drug Calculations Practice Problems Part 6 Youtube
Loading Dose Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
Half Life Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube